Address: 563 Nui Thanh, Hoa Cuong Ward, Da Nang City
Tel: 0916.860.231 - 0905.160.231 - Website: davitecco.com - Email: info@davitecco.com
Warehouse: Thach Nham Dong Village, Ba Na Commune, Da Nang City
Promotion price Contact
Condition of productsIn stock
Description:
Calcium silicate board is an asbestos-free thermal insulation product that can withstand continuous operating temperature from 650C up to 1100C. It is light weight, low thermal conductivity, high strength, easy to install, reliable and durable. There are 3 grades available namely 650 &1000 & 1100 which are commonly used as furnace backup insulation in steel, petrochemical, ceramic, cement & glass industry or fire protection in building construction. It not only provides energy saving, also increases production efficiency and gives personnel protection in industrial safety aspect. And in the housing construction Calcium Silicate Board is also used as the ceiling, fireproof and heat insulation materials of wall and sound absorption materials of decoration.
Applications:
Reheating furnace -Annealing furnace-Transfer ladle -Rotary kiln-Glass tank Dip tubes and spouts Nozzles -Shuttle kiln -Tunnel kiln -Aluminum melting and holding furnace- Distribution boxes, Flow gates Hot pipe supports-Other high temperature ovens or heat processing equipments
Recommendable applications:
- Commercial building: Commerce mansions, entertainment sites, shopping malls and hotels
- Industrial building: Factories and warehouses
- Residential building: New residential housing, renovation and decoration
- Public place: Hospitals, theater and bus stations
- Key Specifications/Special Features:
Specifications:
650 & 1000 C 600-1000 mmX 300-500mm X 25-100mm Speicial deimension will be as per customer request
Technical data:
Standard Type Calcium Silicate Products
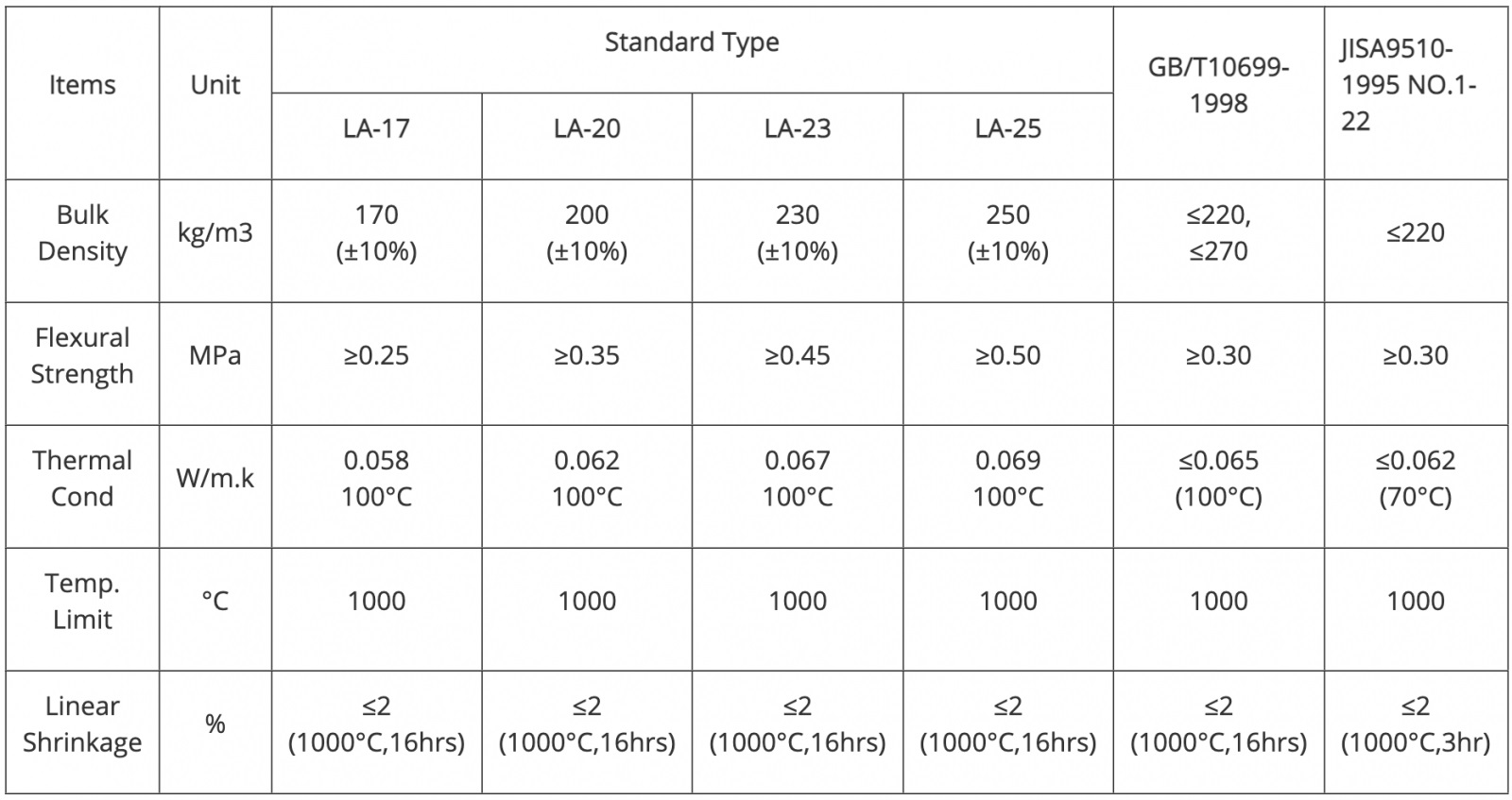
Products with max. service temp. of 650°C are also produced.
High Temp Type Calcium Silicate Products
|
Based on 1000°C Standard Type,the temp. limited of this type is improved to 1100°C. As our paten, High Temp. Type can be used for high temp position of industrial furnaces.. |
|||
|
Items |
Unit |
LA-25 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Bulk Density |
kg/m3 |
250±10% |
|
|
Flexural Strength |
MPa |
≥0.50 |
|
|
Temp. Limit |
°C |
1100 |
|
|
Linear Shrinkage |
% |
≤2(1050°C,3hrs) |
|
|
Themal Cond |
W/m·k |
≤0.069 |
|

1. Are you a manufacturer or trader?
Factory + trade (mainly factories, at the same time, we operates other related products)
2. Can we visit your factory?
Sure,welcome at any time,seeing is believing
3. what's the MOQ of trial order ?
No limit,We can offer the best suggestions and solutions according to your condition.
4. Which payment terms are you accept?
T/T,LC,Western Union,moneygram,Paypal are available for us.
5. After an order is placed, when to deliver?
15-25 days
6. Is your company accept customization?
We have own factory and excellent technical team, and we accept OEM service.
7. How about your company's certification?
SGS,ISO9001 and Test Report,also we could apply other necessary certification.
8. How to solve the quality problems?
If the products are not conform to customer samples or have quality problems, our company will be responsible to make compensation for it.
Promotion
Specializing in Mineral wool products, Rockwool, Glass wool, Insulation products, Vulcanized rubber, Soundproofing products, Refractory brick products, Industrial ventilation, Valves and pipe fittings, Copper pipes & copper pipe fittings, Burners & burner accessories
Currently, the price of Ceramic fiber in sheet form is a topic that many people ...